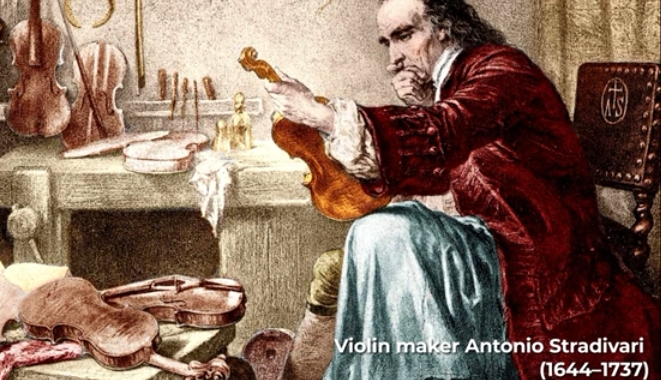Pre historic men shouted for joy or howled with rage. This may have been the beginning of Music, but how did it evolve to what we hear today?
Music was so important to ancient men that they believed god had sent it to them. The oldest civilized men such as the Egyptians, Greeks, Chinese, Hebrews and Hindus all believed that music had come from heaven. The word “Music” is taken from the name of the daughter of Zeus and Muses. Who governed all the beauty and the harmony in the world according to Greek Methodology. Ancient men associated music with magic and used it to pray to the gods. They shouted, clapped with their chests, stomped their feet as they believed that it brought them rain, cured the sick and made crops grow. The very first musical instruments are believed to be rattles of pods and dried seeds, drums made of stretched skin on hollow logs, symbols and gongs from beaten metals and xylophones from rows of different sizes of stones.
Western Music mainly refers to the type of music that originated around Europe. The history of music evolved with style, form, and accompaniment into different types of genres. This evolution has been broken down into different periods as follows;
The Middle Ages (450 – 1400)
The Renaissance period (1400 – 1600)
Baroque Period (1600 – 1750)
Classical Period (1750 – 1820)
Romantic Period (1820 – 1910)
Modern Period (1910 onwards)
Middle Ages
In the early middle ages, music was “Monophonic”. Monophonic means ‘a single voice or a single melody line’. They had no rhythm, written in Latin and based on sacred texts like the bible. For Example; The Gregorian Chant.
In Europe it was the Roman Catholic church that held most of the power at this time and as a result music evolved around the church. Originally music had no rhythmic structure. As music became more complex, there was a need for rhythmic unity. With this complexity, rhythm was notated too.

The Renaissance
With the invention of the printing press and other innovative ideas of the renaissance period, music changed and spread like wildfire. ‘Chants’ grew into music with 2 to 4 parts. While church music continued to grow, musical life was linked to power and royal courts. Vocal music was more important than instrumental music. There was more rhythm in music compared to the Middle Ages. Nevertheless, music was mostly used for religious purposes.

Baroque Period
Music during this period was know as “Polyphonic”. Poly meaning ‘Many’ and Phony meaning ‘Sound’. Composers during this time generally enjoyed the benefits of increased arts patronage as well as the growing acceptance of non-scared instrumental music which fuelled innovation and experimentation. Compositions became more complicated, highly decorated and reached emotional extremes. The musical trends coming out of Italy served as the greatest source of inspiration for baroque composers and many of the practices established by these trends remain in standard to this day. Many instruments that became staples in the modern classical orchestra either matured or were invented during the baroque period.
Bartholomeo Cristofori invented the ‘Pianoforte’ or ‘Fortepiano’ (piano)
Famous Composers during the Baroque Period
- D. Scarlatti
- G. F. Handel
- J.S Bach
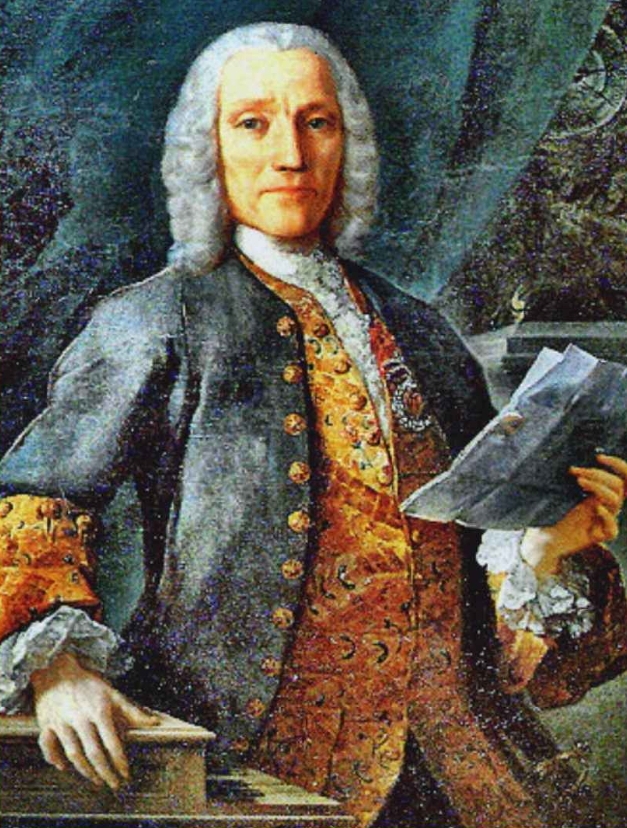

D. Scarlatti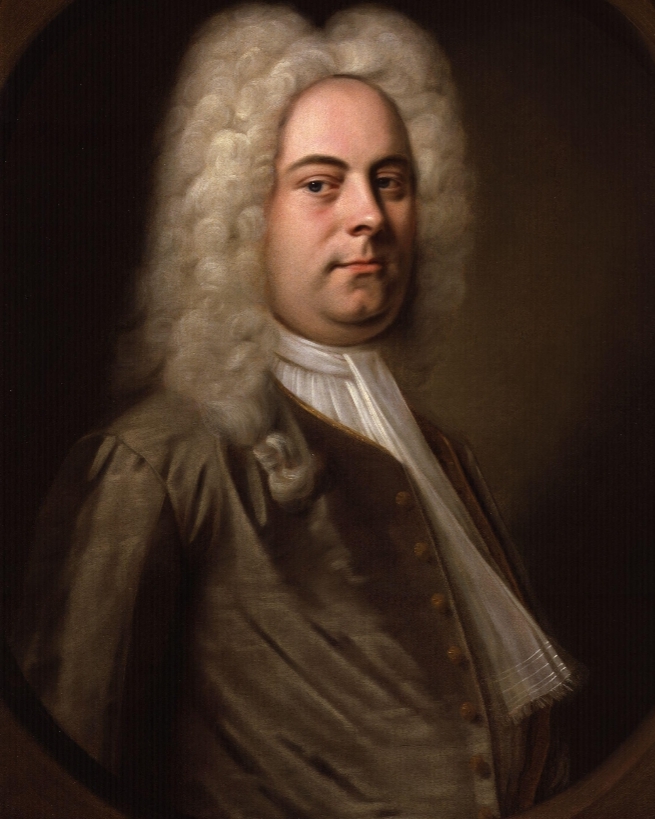 
G. F. Handel 
J.S Bach
Classical Period
Classical Music was based on the western art tradition. This music tradition covers different styles, trends and sounds. Many of the traditional practices of western music were codified during this period. The genres of the orchestral symphony and string quartet began during the classical period and became essential genres for many composers. Orchestral instrumentation likewise became standardised during this period as opposed to earlier periods where composers would simply write for whatever instruments were available at the church or court. These newly standardised forms became the authoritative versions that musicians continued to use and expand upon.

(String Quartet)
Vienna was home to the classical period and the instrument form “Sonata” dominated that period. Compared to the baroque period, classical music had more of a formal balance and singable melodies. These tuneful melodies and simpler textures also appealed to a raising population of new audiences. Musicians no longer had to rely solely on the church or court to perform their music. Public concert houses were being established for the first time. Allowing more people to hear concert music. As a result, music was associated around big concert halls where people used to attend symphonies and operas dressed in tuxedos and fancy dresses.
Famous Composers during the Classical Period
- F . J . Haydn
- W . A . Mozart
- L. V. Beethovan

F . J . Haydn 
W . A . Mozart 
L. V. Beethovan
Romantic Period
Musical romanticism was influenced by the romantic movement in art and literature that began in the late 1700s. The romantics reacted to the growing rationalism of the 18th century, choosing to emphasize on the importance of individual and emotional experiences. Of the many emotional experiences highlighted, the most common was ‘Longing’. Longing for love that was unattainable, longing for a homeland to return to or longing for a better life. This time period along with romanticism also coincides with important political and economical changes in the Europe and America. Political revolutions of the late 1700s sought to give more rights to individuals. In these revolutions the rights of the individuals and their longing for freedom were valorised (Slave Trade abolished in 1807).
As a result of the industrial revolution more people were making money. This created a new middle-class society. The rise of this middle-class society meant that it was no longer only the royalty that had disposable incomes and access to leisure activities and the population of music lovers who could afford to attend concerts and take lessons increased rapidly. To fulfil the demands created by this new middle-class society, music was created in greater quantity for people to enjoy in their homes.
Musicians of the romantic period chose to depict stories tied closely to the individual and to emotional expression. However, unlike the popular plays and operas of the previous century the plots of romantic stories tended to end tragically. In connection to the political changes during the period many composers took part in political movements and wrote pieces to celebrate their country or national identity.

Composers extended the instrumentation they used in their compositions. This included increasing orchestra size to have larger string sections. Composers also added higher and lower instruments to the orchestra to increase its pitch range. The range of the piano was also expanded during the romantic period. Increasing in size from a 4 to 5 octave range to the modern day 7 octave range.

Concert life flourished during the romantic period. The public concerts that have been gaining popularity in the classical period exploded. Governments as well as music societies scheduled concert series to be held throughout the year in a variety of venues. Large concert halls were erected to accommodate large performing orchestras and huge audiences. Composers could now earn money from the performance and publication of their work for such public concerts rather than for composing solely for noble patrons or churches.

Famous Composers during the Romantic Period
- F . Schubert
- F . Mendelssohn
- R. Wagner
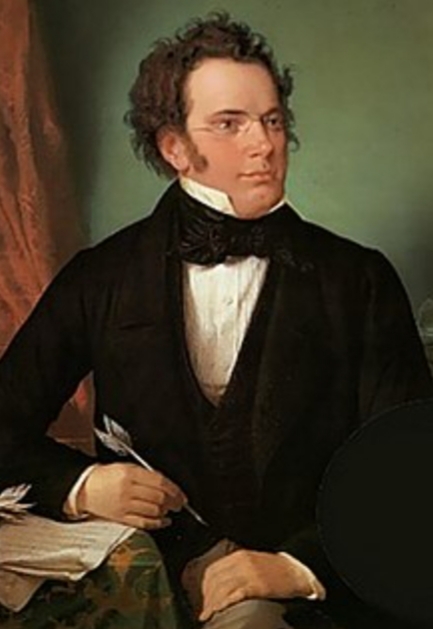

F . Schubert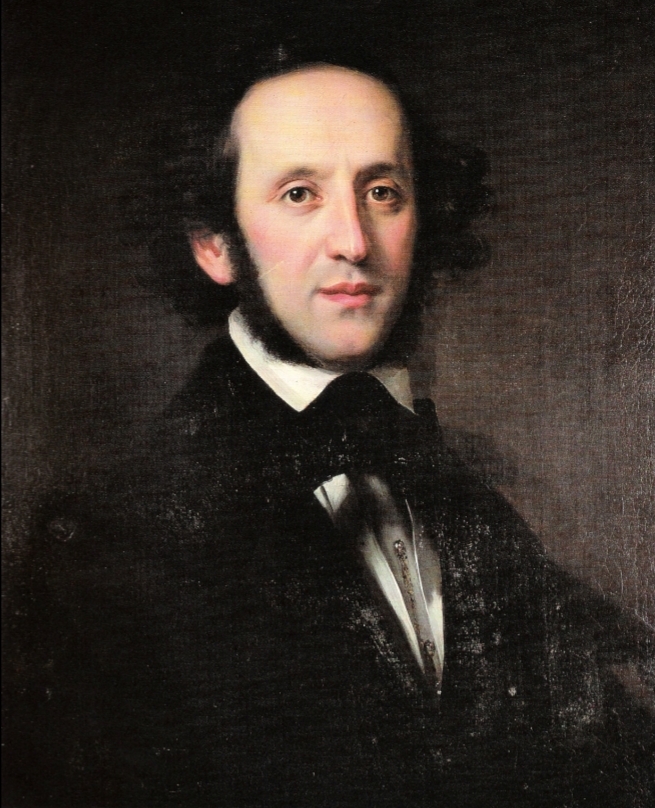 
F . Mendelssohn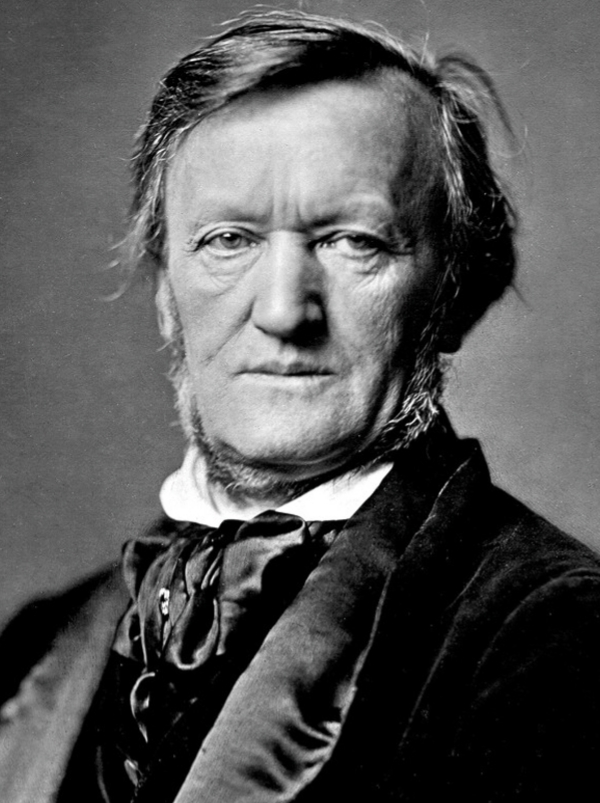 
R. Wagner
Modern Period
As with romanticism, modernism is both a historical time period as well as a philosophical aesthetic. As a term reference in music, modernism was first used by critics to describe forms of musical expression adhering to the radical changes happening at the end of the 19th century. Modernism describes relatively few unifying musical traits. Making it especially useful for referencing many musical styles to grow out of the historical era. The sounds of modernism ranged from the wistful and bucolic to the bizarre and jarring. Modernism derived great inspiration from the social and political upheaval that happened during that period for example, Spanish and American war, 1st world war, the great depression as well as great science achievements such as the theory of evolution, automobiles, recorded sound etc.

The War 
The Great Dpression
Modernise composers thus began to challenge what was possible to do with music. Experimenting with a variety of ways of constructing music. Advancing music through sound experiments. Many of these composers experimented with musical sound through tampers, rhythms and tonality. 4 of the most prominent styles of modernism are Impressionism, Primitivism, Neoclassicism, Atonality.
Famous Composers during the Modern Period
- B. Bartok
- I. Stravinsky
- B. Britten
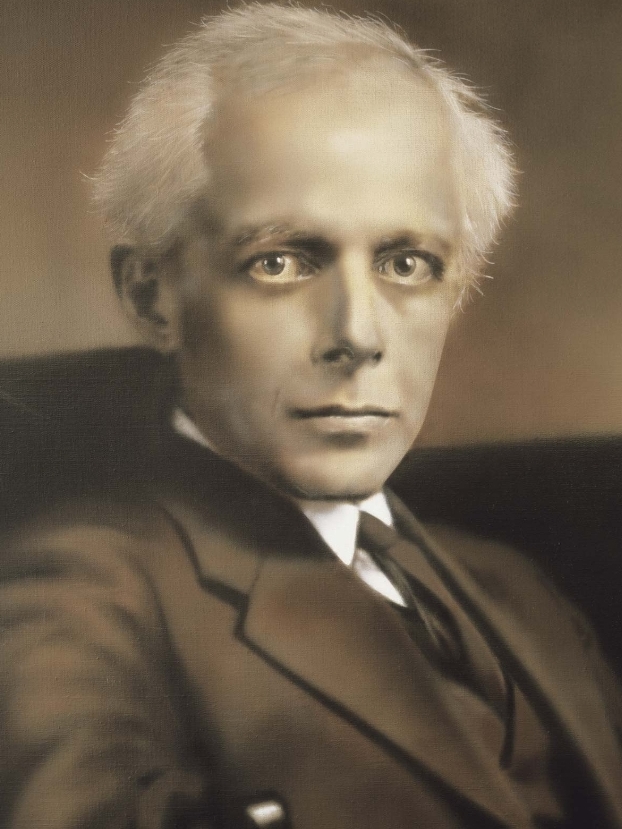

B. Bartok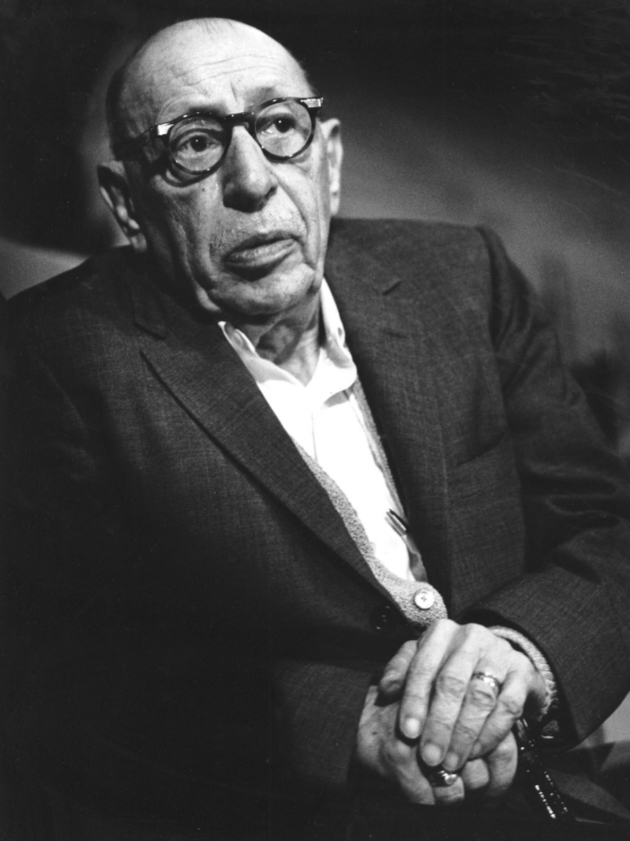 
I. Stravinsky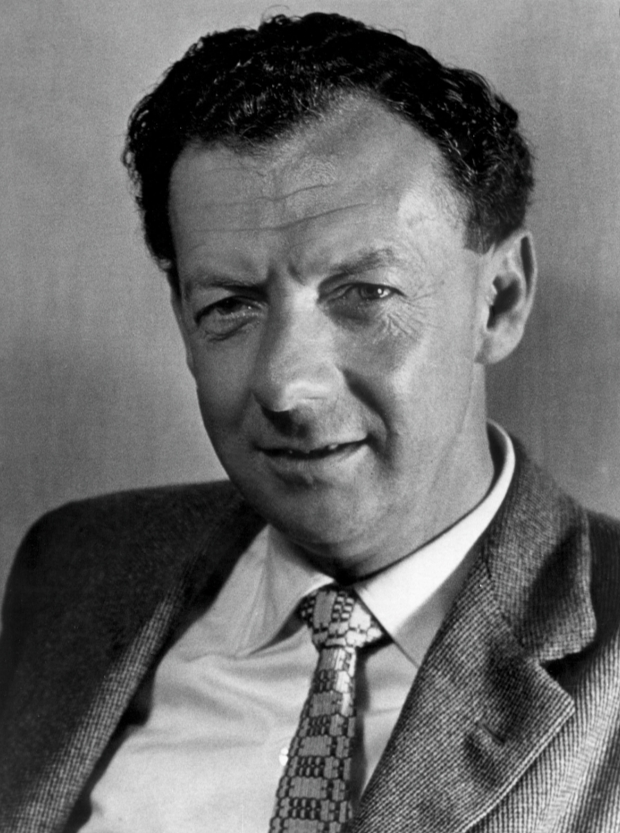 
B. Britten
Written by: Rtr. Dinithi Wijayaratne
Edited by: Rtr. Abinaya Sritharan